Self Evaluation Quiz
This self evaluation quiz has been developed in order to allow every interested potential applicant to evaluate her or his eligibility to study sucessfully the master course on pharmaceutical biotechnology.
Especially the chemical calculations (stoichiometry) in questions 7 - 11 are the foundations of the lab courses.
At least 12 of 16 questions should be correctly answered. If you are unable to answer directly, please have a look to a text book before pressing the "show answer" button!
Important notice: Java Script has to be enabled for correct functionality.
Question 1:
List general differences between a prokaryotic (E. coli) and a eukaryotic (yeast) cell.
Answer to Question 1:
Many answers are possible, such as:
- Eukaryotic cells are (usually) larger, e.g. the nucleus of a yeast cell approximates the size of E. coli
- prokaryotic cells (at least the vast majority) do not contain organelles such as mitochondria, nucleus, Endoplasmatic Reticulum or Golgi apparatuse
- Eukaryotic cells contain always a cytoskeleton
- 70S ribosome in cytoplasm of prokaryotes, 80S ribosomes in cytoplasm of eukaryotes
- in eukaryotic cells, DNA is bound by protein (histones) to form chromatin and packed into the nucleus
- prokaryotic chromosomes are (usually) circular, eukaryotic chromosomes are linear
Question 2:
What are the 4 principle structural elements of a protein?
Answer to Question 2:
- Primary structure: amino acid sequence
- Secondary structure: local substructures, such as α-helix and β-strand
- Tertiary structure: 3-dimensional structure (fold) of a single peptide chain
- Quarternary structure: Assembly between protein molecules
Question 3:
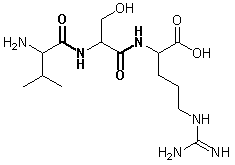
Draw the chemical structure of the tripeptide Val-Ser-Arg and mark the peptide bonds. Denote the side-chain polarity and (if applicable) the side chain charge at pH 7.
Answer to Question 3:
- Val: Polarity: nonpolar - charge: neutral
- Ser: Polarity: polar – charge: neutral
- Arg: Polarity: polar – charge: positive
Question 4:
What is the fluid that fills the nucleus called?
Answer to Question 4:
karyolymph or nucleoplasm
Question 5:
What are the main components of the cytoskeleton?
Answer to Question 5:
microtubules, microfilaments and intermediate filaments
Question 6:
What is pinocytosis?
Answer to Question 6:
"cell drinking". One form of endocytosis. Entrance of small particles and extracellular fluid into the cell engulfed by portions of the cell membrane. Then invagination and detachment of vesicles into cytoplasm.
Question 7:
The following solutions of a drug (mw 316 g/mol) have been prepared. Which one has the highest concentration?
- 3.45 μmol/mL
- 3.56 mM
- 1.2 mg/mL
Answer to Question 7:
3. 1.2 mg/mL
Question 8:
For an enzymatic assay, 800 μL buffer, 150 μL 25 mM substrate solution and 50 μL enzyme solution are mixed.
Please calculate the substrate concentration at the start of enzyme reaction. Give 2 decimal place!
Answer to Question 8:
3.75 mM
Question 9:
You have measured an absorption of 1.78 in a standard cuvette. The disolved substance has an molar absorption coefficient of 6.22 cm²/μmol.
What is the concentration [μM] of the substance? Give 2 decimal places!
Answer to Question 9:
286.17 μM
Question 10:
You have a 2%-solution (w/v) of ampicillin (mw 349.41 g/mol). You need 1 L of a 25 μM solution.
How much mL of the stock solution is necessary? Give 3 decimal place!
Answer to Question 10:
0.437 mL
Question 11:
Calculate the pH of a Tris-buffer. 435.96 mg of Tris and 3.0 mL of 1 M HCl are disolved and diluted to 100 mL with water.
The mw of Tris = 121.1 g/mol and has a pKa = 8.3. Give 2 decimal place!
Answer to Question 11:
pH = 7.60
Question 12:
How much glycerol (mw 92 g/mol) is present in 75 mL of a 5% (w/v) glycerol solution?
Give the result in [g] and [mol]! Give 3 decimal places!
Answer to Question 12:
3.750 g and 0.041 mol
Question 13:
What is the name of this equation?
V = (Vmax * S) / (KM + S)
- Monod
- Hanes
- Michaelis and Menten
- Lineweaver and Burk
- Eadie
Answer to Question 13:
3. Michaelis and Menten
Question 14:
Give the usual definition of one katal enzyme activity!
One katal is defined as the amount of the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of
- 1 µmol of substrate per min
- 1 mmol of substrate per s
- 1 mol of substrate per s
- 1 mmol of substrate per min
(under optimal conditions: T, pH, [S])
Answer to Question 14:
3. 1 mol of substrate per s
Question 15:
The primary structure of proteins:
- refers to three-dimensional structure of a single protein molecule
- is stabilized by the same non-covalent interactions
- refers to highly regular local sub-structures
- refers to amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain
- refer to short segments of protein three-dimensional structure
Answer to Question 15:
4. refers to amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain
Question 16:
Which statement(s) is/are wrong?
- In the protein synthesis only α-amino acids are used.
- In the protein synthesis only α-L-amino acids are used.
- naturally occuring peptides contain only α-amino acids.
- naturally occuring peptides do not contain β-amino acids.
- naturally occuring peptides contain also D-amino acids.
Answer to Question 16:
3. naturally occuring peptides contain only α-amino acids.
4. naturally occuring peptides do not contain β-amino acids.